The lungs are highly repairable, and the vast majority do not have sequelae.
People have a total of two lungs, one on the left and one on the right. But they are not perfectly symmetrical. The right lung has three lobes and the left lung has two lobes.
The main function of the lungs is to exchange air. Through respiration, oxygen from the air is exchanged through the lungs into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed from the body. That’s why it can feel difficult to breathe when there is a serious problem with the lungs.
The lung is an internal organ, to understand the nature and location of lung lesions, the more common approach is to take a CT scan of the lung, through the CT scan of the three-dimensional reconstruction, doctors can better assess the lesions, and formulate more accurate treatment plan. From the new pneumonia autopsy reports that have been published so far, it is clear that critical death cases have lung damage. According to the discharge criteria of the sixth edition of the medical protocol, the lung CT of discharged patients should show significant improvement in absorption; it is also recommended that patients should go to the hospital for follow-up and consultation in the second and fourth weeks after discharge.
![clip_image002[1] clip_image002[1]](https://unicestyle.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/clip_image0021_thumb-2.jpg)
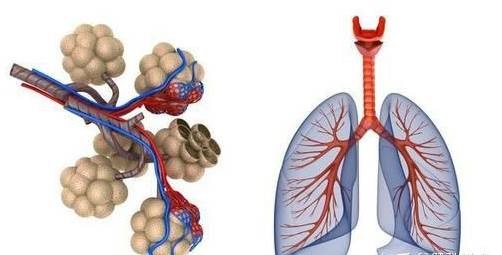
The body’s normal alveoli, where gas exchange takes place
The problem with critically ill patients is not “lung engulfment.”
According to the CDC’s case statistics of more than 70,000 patients with new coronary pneumonia, 81% of the patients were mild/moderate, severe disease accounted for about 14%, and only 5% were critically ill. The diffuse solid lesions in both lungs of critically ill patients are not a direct attack of the virus on the lungs, but an overreaction of the autoimmune system.
After systematic treatment, the patient’s lung function can be gradually restored.
According to the observations of the Radiology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, the vast majority of patients with the new pneumonia were treated with narrower lesions, progressively lower density, fewer lesions, and complete absorption of the milled glass shadow.
Healing and rehabilitation of critically ill patients
After discharge from the hospital, patients with new crowns require rehabilitation, including regaining strength and lung function as soon as possible.
Particularly for patients who have been cured of severe neo-coronary pneumonia, if some lung fibrosis remains and lung function has not fully recovered, i.e., there is dyspnea, decreased exercise tolerance, and limited activity, all of which are indications for the need for rehabilitation therapy.
Patients can rehabilitate themselves in the following ways
1、Lung function exercise
Patients with neo-coronary pneumonia primarily have increased alveolar effusion, which affects alveolar oxygenation. Pulmonary rehabilitation focuses on pulmonary function exercises to open the airways and improve ventilation and lung capacity. The common methods of pulmonary function exercise are lip retraction and abdominal breathing, as follows.
Inhalation and exhalation time ratio is 1:2, 3 to 4 times a day, 10 minutes each time.
Abdominal breathing: The patient’s hip and knee joints are lightly flexed and the whole body is in a comfortable position. One hand is placed on the abdomen and the other on the chest, and lip retraction breathing is performed, with the abdomen raised on inhalation and retracted on exhalation, for 5-10 minutes.
2、Body movement
The main form of rehabilitation exercise is aerobic exercise, the main goal of which is to increase the patient’s overall endurance and improve cardiopulmonary function. Jogging, tai chi, fitness running, cycling and other forms of aerobic exercise are recommended.
3. Balanced nutrition and diet
Consume foods rich in high-quality protein, vitamins, and trace elements, and eat appropriate foods that nourish the lungs, such as pears and lilies.
4. routine to improve the home environment
Pay attention to air circulation to avoid irritation from harmful gases, smoke and dust. Promote anti-smoking to create a smoke-free environment. Patients should pay attention to the cold and warmth to prevent colds.